Unit 4 study guide congruent triangles – Welcome to Unit 4: Congruent Triangles, an engaging study guide that delves into the fascinating world of triangle congruence. As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the intricacies of congruent triangles, their properties, applications, and the common misconceptions surrounding them.
Get ready to expand your geometric knowledge and sharpen your problem-solving skills as we explore the captivating realm of congruent triangles.
Definition of Congruent Triangles: Unit 4 Study Guide Congruent Triangles
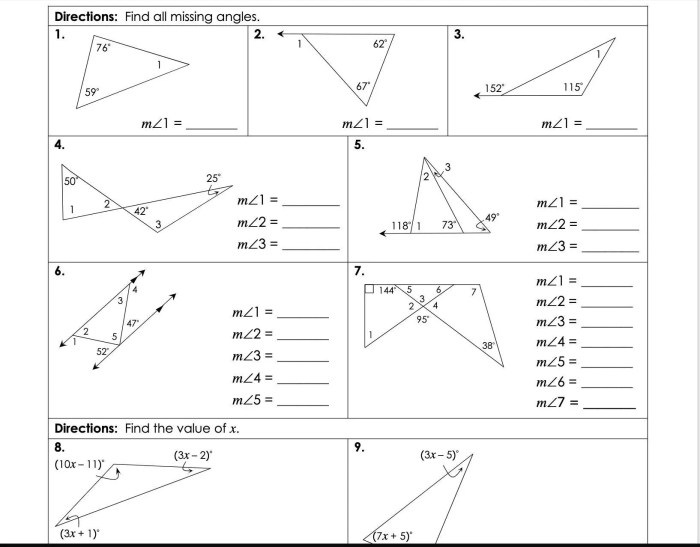
Congruent triangles are two triangles that have the same shape and size. They have the same three sides and the same three angles. This means that the corresponding sides and angles of congruent triangles are equal.
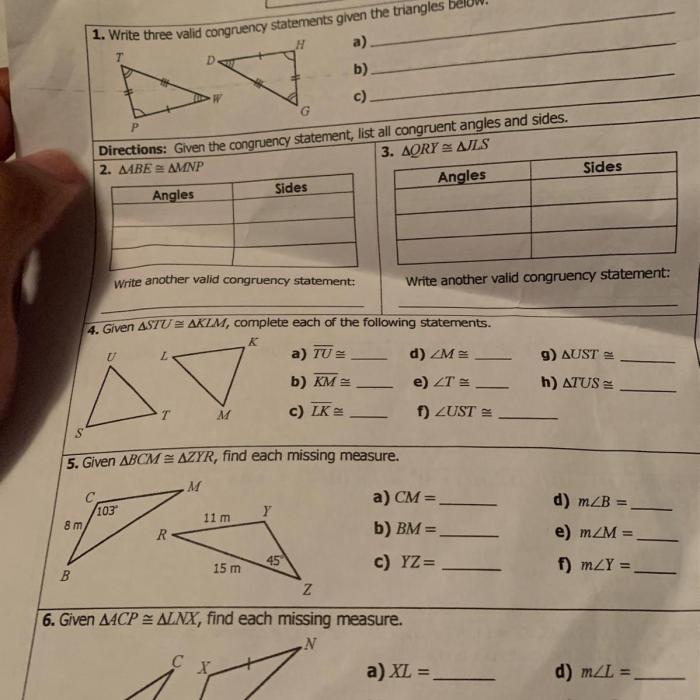
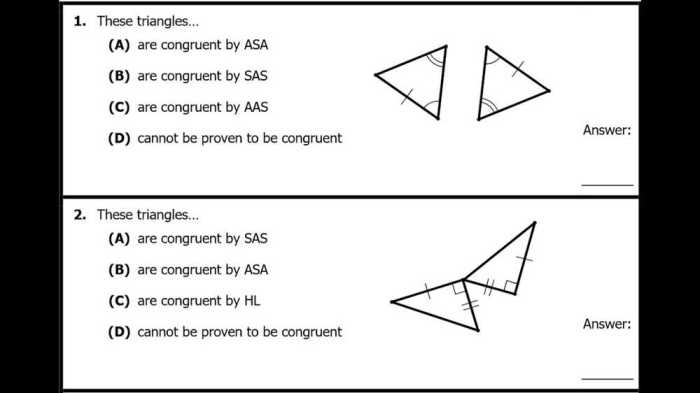
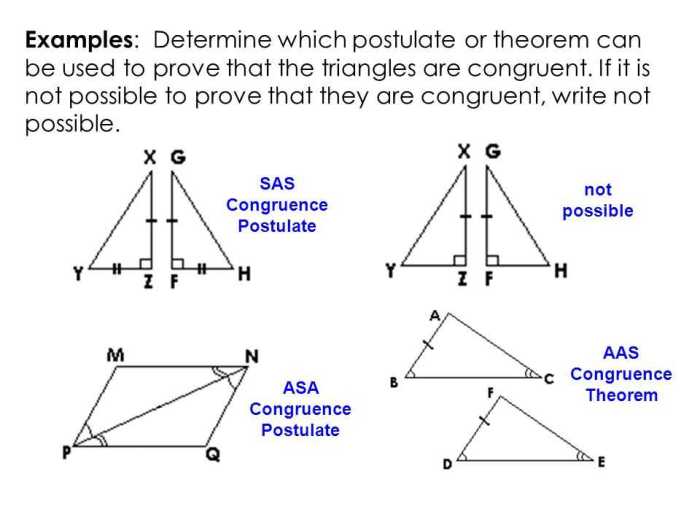
There are three conditions that make triangles congruent:
- SSS (Side-Side-Side): If the three sides of one triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side): If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
- ASA (Angle-Side-Angle): If two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to two angles and the included side of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
Properties of Congruent Triangles
Congruent triangles have several important properties:
- The corresponding sides of congruent triangles are equal.
- The corresponding angles of congruent triangles are equal.
- The corresponding medians of congruent triangles are equal.
These properties can be used to prove triangles congruent. For example, if you can show that the three sides of one triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, then you can conclude that the triangles are congruent by the SSS condition.
Applications of Congruent Triangles, Unit 4 study guide congruent triangles
Congruent triangles have many applications in real life. For example, they are used in:
- Architecture: Congruent triangles are used to design buildings and other structures that are symmetrical.
- Engineering: Congruent triangles are used to design bridges and other structures that need to be strong and stable.
- Design: Congruent triangles are used to create patterns and designs in art and fashion.
Understanding congruent triangles can also help you solve problems and make calculations. For example, you can use congruent triangles to find the area of a triangle or to find the distance between two points.
Common Misconceptions and Errors
There are some common misconceptions and errors related to congruent triangles. For example, some people believe that all triangles with equal sides are congruent. However, this is not true. Triangles can have equal sides but not be congruent if their angles are not equal.
Another common error is to assume that triangles with equal angles are congruent. However, this is also not true. Triangles can have equal angles but not be congruent if their sides are not equal.
It is important to avoid these misconceptions and errors in order to understand congruent triangles accurately.
Questions and Answers
What are congruent triangles?
Congruent triangles are triangles that have the same shape and size. This means that their corresponding sides and angles are equal in measure.
What are the conditions for triangle congruence?
There are four conditions that make triangles congruent: SSS (Side-Side-Side), SAS (Side-Angle-Side), ASA (Angle-Side-Angle), and AAS (Angle-Angle-Side).
How can I prove triangles congruent?
To prove triangles congruent, you can use the SSS, SAS, ASA, or AAS conditions. You can also use the properties of congruent triangles, such as the fact that corresponding parts are congruent.